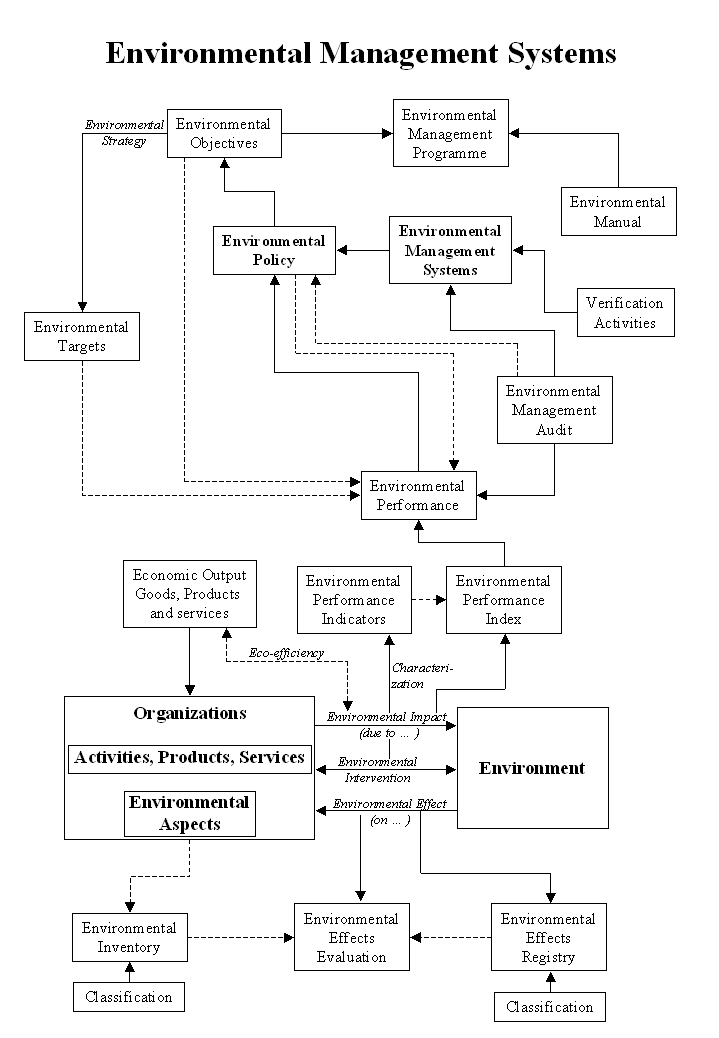
Glossary of Environmental Terms
The use of these terms and definitions varies largely
from one author to another. The list below relies on definitions used by
internationally recognized organizations (e.g. ISO,
SCC, SETAC),
environmental agencies (e.g. Environmental
Protection Agency of the USA) or research reports of large groups of
scientists and projects etc.
- Abiotic Resources
- Resources which are considered abiotic
and therefore not renewable. Zinc ore and crude oil are examples of abiotic
resources.
- Ancillary Material
- Material that is not used directly in the formation of a product or
service.
- Auditing
- See environmental management system audit.
- Biotic Resources
- Resources which are considered biotic
and therefore renewable. The rainforests and tigers are examples of biotic
resources.
- By-Product
- A useful and marketable product or service that is not the primary
product or service being produced. See also co-product.
- Certification
- The procedure by which third party gives written assurance that a
product, process, or service conforms to specific requirements.
See also registration.
- Characterization
- Characterization aggregates classified
environmental interventions/aspects
within an environmental impact category. This step results in environmental
performance indicators.
- Characterization Factor
- A factor that describes the relative harmfulness of an environmental
intervention within one environmental impact
category. A factor is a result of modeling environmental
effects/problems.
- Classification
- Classification attributes are environmental
interventions/aspects listed in an environmental
inventory/environmental effects register
according to environmental impact categories.
- Close-loop Recycling
- A recycling system in which a product
made from one type of material is recycled into a different type of product
(e.g. used newspapers into toilet paper). The product receiving recycled
material itself may or may not be recycled. See also open-loop recycling.
- Co-Product
- A marketable by-product from a process
that can technically not be avoided. This includes materials that may be
traditionally defined as waste such as industrial
scrap that is subsequently used as a raw material in a different manufacturing
process.
- Continuous Improvement
- The process of enhancing an environmental
management system to achieve improvements in overall environmental
performance in line with an organization's
environmental policy.
- Damage
- A deterioration in the quality of the environment not directly attributable
to depletion or pollution.
- Depletion
- The result of the extraction of abiotic resources
(non-renewable) from the environment or the
extraction of biotic resources (renewable) faster
than they can be renewed.
- Downcycling
- See recycling.
- Eco-Efficiency
- The relationship between economic output (product, service, activity)
and environmental impact added caused by production,
consumption and disposal.
- Emission
- One or more substances released to the water, air or soil in the natural
environment. See also environmental release,
pollution and environmental
intervention.
- Environment
- Surroundings in which an organization
operates, including air, water, land, natural resources, flora, fauna, humans,
and their interrelations. This definition extends the view from a company
focus to the global system.
- Environmental Aspects
- Elements of an organization's activities,
products or services which can interact with the environment
(ISO 14004). A significant environmental
aspect is an environmental aspect which has or can have a significant environmental
impact. See also environmental
interventions, environmental problem.
- Environmental Effect
- Any direct or indirect impingement of activities, products and services
of an organization upon the environment,
whether adverse or beneficial. An environmental
effect is the consequence of an environmental intervention
in an environmental system. See also environmental impact,
environmental problem.
- Environmental
Effects Evaluation
- A documented evaluation of the environmental significance of the effect
of an organization's activities, products and
services (existing and planned) upon the environment.
- Environmental Effects Register
- A list of significant environmental effects,
known or suspected, of an organization's activities,
products and services upon the environment. Also see environmental inventory.
- Environmental Impact
- Any change to the environment, whether
adverse or beneficial, wholly or partially resulting from an organization's
activities, products or services. An environmental impact addresses an environmental
problem. Also see environmental effect.
- Environmental Impact Added
- The total of all environmental interventions
of a product or production system evaluated (weighted) according to the
harmfulness of each intervention to the environment.
- Environmental Intervention
- Exchange between the economy and the environment
including resource extraction, emissions to
the air, water, or soil, and aspects of land use. If resource extraction
is excluded, the term used in this case is environmental
release. See also
emission and pollution.
- Environmental Inventory
- An environmental inventory identifies and quantifies - where appropriate
- all environmental aspects of an organization's
activities, products and services. Also see environmental
effects register.
- Environmental Issue
- A point or matter of discussion, debate, or dispute of an organization's
environmental aspects.
- Environmental Management
- Those aspects of an overall management function (including planning)
that determine and lead to implementation of an environmental
policy. See also environmental
management system.
- Environmental
Management Audit
- A systematic evaluation to determine whether an environmental
management system and environmental performance
comply with planned arrangements, and whether a system is implemented effectively,
and is suitable to fulfill an organization's
environmental policy.
- Environmental
Management Manual
- The documentation describing the procedures for implementing an organization's
environmental management program.
- Environmental
Management Program
- A description of the means of achieving environmental objectives
and targets.
- Environmental
Management Review
- A formal evaluation by management of the status and adequacy of systems
and procedures in relation to environmental issues, policy and regulations
as well as new objectives resulting from changing circumstances.
- Environmental
Management System
- The part of an overall management system
which includes structure, planning activities, responsibilities, practices,
procurements, processes and resources for developing, implementing, achieving,
reviewing and maintaining an environmental policy.
- Environmental
Management System Audit
- A systematic and documented verification process
to objectively obtain and evaluate evidence to determine whether an organization's
environmental management system conforms to
the environmental management system audit criteria set by the organization,
and communication of the results of this process to management.
- Environmental Objectives
- The overall environmental goal, arising from an environmental
policy, that an organization sets itself
to achieve, and which is quantified where practical.
- Environmental Performance
- Measurable results (see environmental performance
indicators/index) of an environmental
management system, related to the control of its environmental
aspects. Assessment of environmental performance
is based on environmental policy, environmental
objectives and environmental targets.
- Environmental Performance Index
- A parameter describing environmental impact
with a single figure. An index is usually calculated by weighting the actual
impact level against a target level. Also see
valuation.
- Environmental Performance Indicators
- Different parameters describing the potential impact of activities,
products or services on the environment. These
parameters are the result of characterizing
classified environmental interventions/environmental
aspects.
- Environmental Policy
- A statement by an organization of its
intentions and principles in relation to its overall environmental
performance. Environmental policy provides a framework for action and
for the setting of its environmental objectives
and target.
- Environmental Problem
- An environmental problem is a description of a known process within
the environment or a state of the environment
which has adverse effects on the sustainability of the environment
including society. They
include resource consumption and environmental
impacts. See also environmental effects, environmental
aspects.
- Environmental Regulation Register
- A list of regulations regarding environmental
aspects of an organization. Also see environmental
effects register and environmental inventory.
- Environmental Release
- See environmental interventions.
- Environmental Target
- A detailed performance requirement, quantified where practical, applicable
to the organization or parts or combination
thereof, that arises from environmental objectives
and that must be set and met in order to achieve those environmental
objectives.
- Environmental Strategy
- A plan of action intended to accomplish a specific environmental
objective.
- Interested Party
- Individuals or groups concerned with or affected by the environmental
performance of an organization. Interested groups include
those exercising statutory environmental control over an organization,
local residents, an organization's investors,
insurers, employees, customers and consumers, environmental interest groups
and the general public.
- Open-loop Recycling
- A recycling system in which a particular
mass of material (possible after upgrading) is remanufactured into the same
product (e.g. glass bottles into glass bottles). See also open-loop recycling.
- Organization
- A company, corporation, firm, enterprise or institution, or part or
combination thereof, whether incorporated or not, public or private, that
has its own functions and administration. For organizations with more than
one operating unit, a single operating unit may be defined as an organization.
- Pollution
- Residual discharges of emissions to the
air or water following application of emission control devices (EPA
1993b). See also environmental release
and environmental intervention.
- Primary Product
- The product or service which is the strategic focus of an organization.
See also by-product and co-product.
- Prevention of Pollution
- The use of processes, practices, methods or products that avoid, reduce
or control pollution. These may include reycling,
treatment, process changes, control mechanisms, efficient use of resources
and material substitution.
- Recycling
- The process of re-using material for the production of new goods or
services on the same quality level. If the quality of the goods and services
produced with recycled material is lower, then the process is known as downcycling. See also
close-loop recycling and open-loop
recycling.
- Registration
- The procedure by which an organization indicates relevant characteristics
of a product, process or service, or particulars of an organization or person,
and then includes or registers the product, process, or service in an appropriate
publicly available list. See
also certification.
- Resources
- Materials found in the environment that
can be extracted from the environment in an
economic process. There are abiotic resources
(non-renewable) and biotic resources (renewable).
- Reuse
- The additional use of a component, part, or product after it has been
removed from a clearly defined service cycle. Reuse does not include reformation.
However, cleaning, repair, or refurbishing may be done between uses.
- Solid Waste
- Solid products or materials disposed of in landfills, incinerated
or composted. See also waste.
- System
- A collection of operations that perform a desired function.
- Valuation
- The process of weighting characterized
environmental interventions against each other
in a quantitative and/or qualitative way. This process results in an environmental
performance index.
- Verification Activities
- All inspection, test and monitoring work related to environmental
management.
- Waste
- An output with no marketable value that is discharged to the environment. Normally the term "waste"
refers to solid or liquid
materials.
- Waterborne Waste
- Discharge to water of pollutants.
|