 The Informal Sector
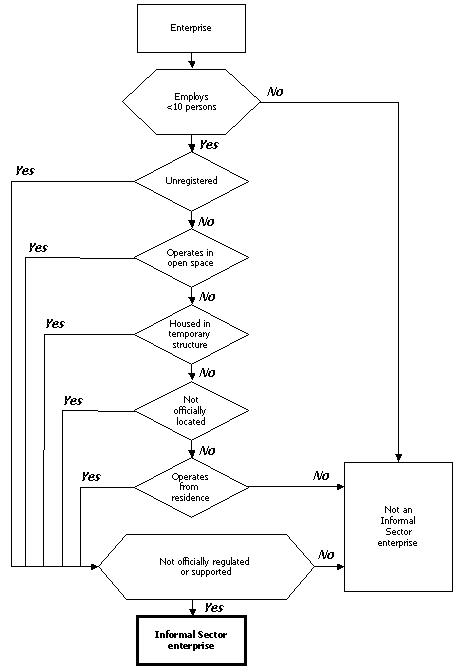
The following flow chart attempts to define the characteristics of enterprises in urban areas, particularly micro-enterprises, that can be called "informal". The flowchart also focuses on the unique features of informal sector enterprises (or 'what it really is'), rather that simply comparing/contrasting it to the characteristics of formal sector enterprises (or 'what it is not').
The flowchart positions a number of criteria that characterizes informal sector enterprises. These include, for example, number of employees or place of operation or registered enterprise.
Ultimately, if a enterprise employees less than 10 persons, satisfies any one of five criteria (unregistered, operates in an open space, housed in a temporary structure, not officially recognized, operates from a residence), and is not officially regulated or supported, then the enterprise can be called an informal sector enterprise.
The flow chart helps in better understanding the conditions within which an informal enterprise functions, and points to the areas where policy should focus on, rather than simply trying to 'eliminate' them since it is not 'formal'. For example, the criteria, "housed in a temporary structure" implies that it is necessary for us to focus positively and proactively on policies that provide good and environmentally safe working spaces, and not just on enforcing rules and standards that do not fit the situation of informal sector enterprises. | |
|